SHREE LEARNING ACADEMY
Man in the Browser
The "Man in the Browser" (MITB) attack is a type of cyber attack that targets web browsers and is designed to steal sensitive information from users. This attack is a variation of the "Man in the Middle" (MITM) attack, in which an attacker intercepts communication between two parties without their knowledge or consent.
In the case of the MITB attack, the attacker inserts malicious code into a victim's web browser. This code is typically delivered through a malware infection or phishing email. Once the code is installed, it enables the attacker to monitor the victim's web browsing activities and to modify the content of web pages displayed in the browser.
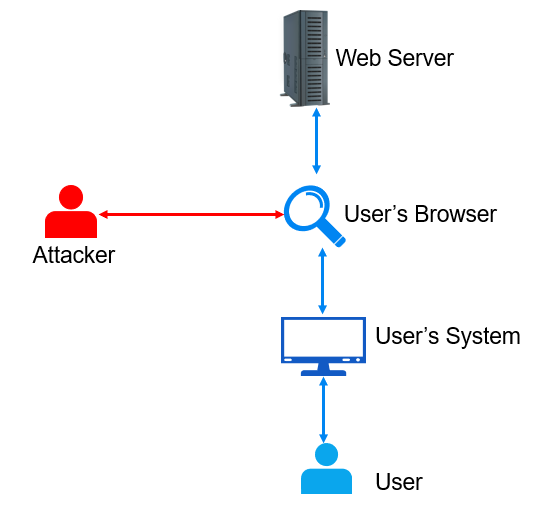
The attack is called "Man in the Browser" because the attacker can insert code that sits between the user and the web server, allowing them to intercept and modify communication between the two. The code is typically injected into the browser in the form of a browser extension, add-on, or plugin, which the victim may install without realizing that it is malicious.
Malicious Add-ons
Downloadable add-ons, BHOs (browser helper objects), plug-ins, or expansion packs are now commonly available for many applications, including web browsers. These extensions provide added functionality and customization options for users. However, they also provide additional targets for attackers seeking to exploit vulnerabilities in these addons for malicious purposes. Attackers have created fraudulent versions of add-ons, transformed legitimate add-ons into Trojan horses, and developed seemingly genuine add-ons that contain malicious code to deceive users.
The objective is to deceive unsuspecting individuals into installing the malicious add-ons, allowing attackers to either obtain sensitive information or acquire control over the victim's identity or system. To tackle this problem, browser add-on stores now mandate the signing of add-ons. However, it is crucial to exercise caution while installing any software, and only opt for trusted sources. Additionally, it's recommended to use up-to-date antivirus and antimalware scanners.
Header Manipulation
Header manipulation is a type of attack that involves the submission of malicious content to a vulnerable application, such as a web browser or web server. The attacker disguises the content as a legitimate HTML/HTTP header value. Typically, header manipulation is utilized as a tactic to achieve some malicious objective, such as cross-user defacement, cache poisoning, cross-site scripting, page hijacking, cookie manipulation, open redirects, and other similar activities. To prevent this type of attack, it is generally necessary to employ updated browsers/servers, implement content filtering for visitors, and reject/ignore any headers that violate HTTP/HTML specifications.
Attacker can:
The malicious code in the browser can enable the attacker to:
Intercept user input:
The attacker can intercept keystrokes, mouse clicks, and other user input, allowing them to steal login credentials, credit card numbers, and other sensitive information.
Modify web pages:
The attacker can modify the content of web pages displayed in the browser, such as changing the amount of a financial transaction or modifying the recipient of an email.
Redirect web traffic:
The attacker can redirect the victim's web traffic to a different website, allowing them to steal sensitive information.
The MITB attack is particularly dangerous because it can bypass traditional security measures such as firewalls and antivirus software. This is because the attack takes place inside the victim's browser, which is often considered a trusted environment.
Security Measures:
Here are some steps you can take to prevent a Man-in-the-Browser attack:
Keep your software up to date:
Regularly update your web browser and any other software you use to stay protected against known vulnerabilities.
Use anti-virus software:
Install and regularly update anti-virus and anti-malware software on your computer to detect and remove any malicious software that could be used in an MITB attack.
Use strong passwords:
Use complex and unique passwords for each online account, and enable two-factor authentication where possible.
Be cautious of suspicious emails and links:
Avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from suspicious emails, as these can often be used to initiate an MITB attack.
Use a VPN:
Consider using a virtual private network (VPN) when connecting to the internet, as this can provide an additional layer of security by encrypting your online activity.
Monitor your accounts:
Regularly check your online accounts and financial statements for any suspicious activity, and report any unauthorized transactions or activity to your bank or financial institution immediately.
By following these steps, you can significantly reduce the risk of a Man-in-the-Browser attack and help keep your personal information safe and secure.
Test Yourself
Take Free Quiz
Watch our Video Tutorial

